Maine Cannabis Market Analysis: Border State Advantage Meets Organized Crime Challenge
Using the CBDT Framework to predict Maine's market trajectory amid organized crime infiltration and recent tax increases
The Silent Majority 420 | November 2025
The Pine Tree State's Paradox
Is weed legal in Maine? Yes—adults 21+ can legally possess 2.5 ounces of cannabis and cultivate 3 mature plants at home. Maine launched adult-use retail sales on October 9, 2020, and currently operates 170+ licensed retail stores serving 1.38 million residents plus substantial cross-border traffic from New Hampshire.
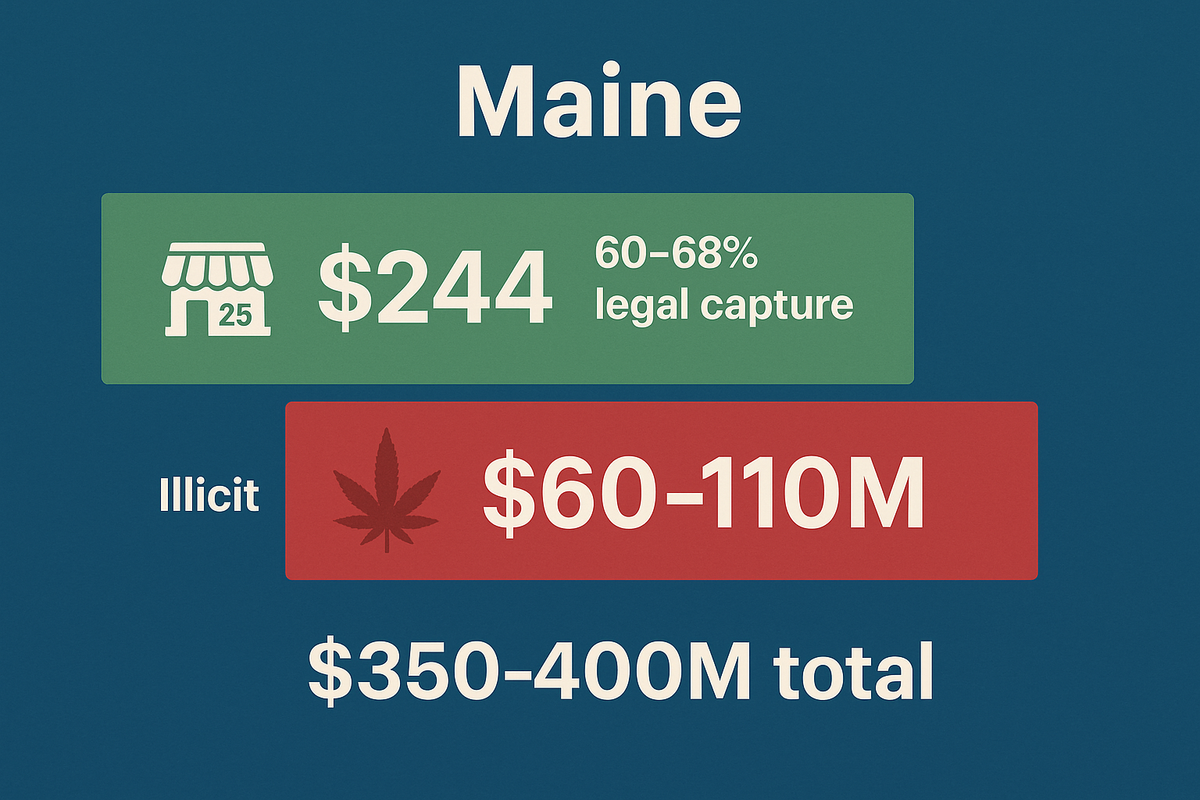
But Maine's cannabis success story contains troubling contradictions. While the state generated $244 million in adult-use sales in 2024 and collected over $500 million in tax revenue since retail launch, law enforcement has identified 100-200 illegal cultivation operations linked to Chinese organized crime networks. Since 2023, authorities raided 60+ grow houses, seizing tens of thousands of plants and discovering 42% of medical cannabis contaminated with banned pesticides that create cyanide gas when smoked.
Then, in June 2025, Maine's legislature passed legislation increasing the adult-use sales tax from 10% to 14%—a 40% tax hike with an effective date of January 1, 2026, intended to address a $450 million state budget deficit. This policy change is codified in 36 MRS §1811(D)(5). This single policy decision will likely reduce legal market share by 6-8 percentage points starting January 2026, undermining years of optimization progress just as the state battles its most serious enforcement crisis since legalization.
The Consumer-Driven Black Market Displacement (CBDT) Framework, validated across 24 U.S. cannabis markets with 5% mean absolute error, reveals Maine currently achieves approximately 65-70% legal market share. However, with the 14% sales tax taking effect January 1, 2026, legal share will likely decline to 58-65% as price competitiveness deteriorates. With enforcement investment and federal reform—plus tax policy correction—Maine could reach 72-78% legal share within 36-48 months. However, the June 2025 tax legislation moved Maine in the wrong direction, demonstrating how fiscal crisis tempts policymakers to sacrifice long-term market optimization for short-term revenue gains.
Framework Validation and Methodology
The CBDT Framework has demonstrated exceptional predictive accuracy:
- Rank-order correlation: r = 0.968 across 24 U.S. states
- Mean absolute error: 5% (out-of-sample validation)
- Oregon prediction: Correctly forecasted ~95% transaction share, 82% volume share
- California prediction: Accurately predicted 50% legal market capture despite early mover advantage
- New York prediction: Validated 30% legal share amid regulatory dysfunction
The framework quantifies five policy levers determining legal market capture:
- Price competitiveness (4× weight—most critical variable)
- Access density (store availability, delivery infrastructure)
- Safety and quality advantage (testing standards, consistency)
- Convenience (payment methods, operating hours, friction reduction)
- Enforcement intensity (illicit supply interdiction)
A sixth variable—market fragmentation—acts as a penalty reducing effective access through local retail bans and geographic barriers.
Validation data: Harvard Dataverse, DOI: 10.7910/DVN/MDVDTQ
Framework methodology: The Black Market Death Equation: Why Cannabis Will Follow Nevada's Path to Single-Digit Illicit Markets
Current Status: Is Weed Legal in Maine?
Adult-Use Cannabis: YES (Legal Since 2016)
Possession Limits:
- 2.5 ounces of cannabis flower
- 5 grams of cannabis concentrate
- Adults 21+ can possess, use, and transport
Home Cultivation:
- 3 mature cannabis plants per adult
- 12 immature plants per adult
- Unlimited seedlings
- Must be grown in private residence or with written landowner permission
- Plants must be tagged with owner's name, ID number, and legal authorization notation
- Important: Municipalities can opt out of allowing home cultivation—check local regulations
- Medical patients can cultivate 6 mature plants + 12 immature + unlimited seedlings
Home Cultivation Economics:
While Maine allows generous home cultivation limits, research demonstrates personal cultivation is neither practical solution nor competitive threat for most consumers. Home growing requires:
- Equipment investment: $300-800 (lights, ventilation, nutrients)
- Electricity costs: $40-80 monthly for flowering
- Time investment: 5-15 hours weekly
- Technical knowledge: Growing quality cannabis requires skill
- Space: Dedicated area with proper ventilation, humidity, temperature control
Most consumers prefer convenient retail purchase at $7-8/gram versus investment and effort for home cultivation. Maine's craft cannabis culture and rural character make home cultivation more common than urban states, but it reduces legal retail share by only 2-4 percentage points.
Public Use:
- $100 fine for smoking cannabis in public spaces
- Consumption must occur in private residences
- No on-site consumption venues—Maine's legislature removed this provision from the 2016 voter initiative despite public approval
- Operating vehicles under influence: Criminal offense with DUI penalties
Penalties for Minors:
- Under 21 with up to 1.25 ounces: $350-600 fine (mandatory, non-suspendable)
- Under 21 with over 1.25 to 2.5 ounces: $700-1,000 fine (mandatory, non-suspendable)
- No jail time for possession-only offenses by minors
Retail Market Structure (2025)
170+ licensed adult-use dispensaries serving Maine's 1.38 million residents—substantial growth from initial 37 stores in 2021
Density: 12.3 stores per 100,000 residents—strong coverage comparable to Oregon (16.8) and well above California (5.2) or Illinois (4.8)
Geographic Distribution:
- York County: 35% of dispensaries (border with New Hampshire—"Green Mile" along Route 1)
- Cumberland County: 25% of dispensaries (Portland metro, second-largest population center)
- Remaining 14 counties: 40% of dispensaries spread across rural areas
Municipal Fragmentation: The 84% Opt-Out Problem
Only ~80 of Maine's 500+ municipalities (16%) allow adult-use retail. This creates severe access barriers forcing majority of residents to travel substantial distances.
"Cannabis Deserts" by Region:
- Northern Maine: Aroostook County (population 67,000) has minimal retail presence despite being Maine's largest county by area
- Western Maine: Franklin and Oxford counties significantly underserved
- Central Maine: Somerset, Piscataquis counties face access gaps
Revenue Sharing Failure: Legislative efforts to incentivize municipal opt-in through 5% revenue sharing have repeatedly failed. In 2022, Legislature passed reimbursement program ($20,000 per municipality for opt-in costs) but removed direct revenue share. From 2022-2024, opt-ins increased modestly from ~60 to ~80 municipalities—insufficient progress.
Impact: This fragmentation particularly disadvantages rural residents, elderly without transportation flexibility, and lower-income consumers unable to absorb travel costs. Many resort to illicit markets or medical program despite preferring convenient adult-use retail.
Tax Structure: January 2026 Increase
CRITICAL UPDATE - Enacted June 2025, Effective January 1, 2026:
Maine legislature passed legislation increasing adult-use cannabis sales tax from 10% to 14% (40% increase) to address $450 million state budget deficit. The new rate takes effect January 1, 2026.
Current Tax Burden (through December 31, 2025):
- Sales tax: 10% on all adult-use retail sales
- Infused products excise: 8% on edibles
- Cultivator excise taxes:
- $335 per pound of flower
- $94 per pound of trim
- $1.50 per immature plant
- $35 per mature plant
- $0.30 per seed
- Total effective burden: ~18-20% (10% sales + 8-10% from cultivator excise built into wholesale prices)
New Tax Burden (starting January 1, 2026):
- Sales tax: 14% on all adult-use retail sales
- Cultivator excise taxes: Same as above
- Total effective burden: ~24-26% (14% sales + 10% from cultivator excise)
Medical cannabis exempt from adult-use taxes, subject only to 5.5% state sales tax (8% for prepared food edibles).
CBDT Impact: The 4-percentage-point sales tax increase (10% → 14%) will reduce legal market share by estimated 6-8 percentage points starting January 2026. Framework analysis shows cannabis consumers are highly price-sensitive—a 10% legal price increase reduces legal market choice probability by 2.3%. Maine currently achieves approximately 65-70% legal share (through December 2025) but will likely decline to 58-65% legal share once the 14% rate takes effect.
2024 Market Performance
According to Maine's Office of Cannabis Policy open data portal, Maine achieved the following performance in 2024:
Sales: $244 million in adult-use sales (up 12% from 2023's $217 million)
Transactions: 4.56 million purchases
Average Price: $7.24 per gram dried flower (down 7% year-over-year)
Tax Revenue: $27.8 million in adult-use collections (2024, at 10% tax rate)—projected to increase to ~$34 million annually at 14% rate starting January 2026, though on smaller transaction base due to reduced competitiveness
Per Capita: $177 annually—mid-tier performance exceeding Illinois ($134) but trailing Colorado ($425)
Growth Trajectory: Year-over-year growth flattening (2% projected 2025 growth) as market matures—expected behavior for fifth-year markets
The Border State Advantage: Capturing New Hampshire Dollars
Maine's most significant structural advantage is geographic: New Hampshire, with 1.4 million residents, has decriminalized possession but offers zero legal retail options.
New Hampshire's Prohibition Subsidy
New Hampshire Policy Status:
- Possession ≤0.75 oz: $100 civil fine (decriminalized 2017)
- Medical program: Exists but very limited (4 dispensaries statewide)
- Adult-use retail: Prohibited
- Home cultivation: Prohibited
Despite New Hampshire's libertarian "Live Free or Die" culture, conservative Republican legislative supermajority maintains adult-use prohibition. Multiple legalization bills have died without floor votes.
Result: 1.4 million New Hampshire residents seeking legal cannabis must travel to Maine (north), Massachusetts (south), or Vermont (west—limited retail).
Border Dispensary Economics
Maine captures substantial cross-border traffic:
York County "Green Mile": Dispensaries cluster along Route 1 in Eliot and Kittery (Maine-NH border towns)
Customer Demographics: Border dispensaries report 60-80% customers from out-of-state, predominantly New Hampshire
Conservative Estimate:
- NH cannabis consumers purchasing in Maine: 58,000-90,000
- Average annual spending: $800-1,000
- Total NH-to-Maine spending: $46-90 million annually
- Maine tax revenue from NH residents: $8-16 million annually (30-60% of total adult-use tax collection)
Pricing Advantage: Maine undercuts Massachusetts by 20-35%:
- Maine average: $7.24/gram ($50-55 per eighth)
- Massachusetts average: $12-15/gram ($35-45 per eighth after taxes)
Massachusetts Competition and Pricing Advantage
Massachusetts legalized adult-use cannabis in 2016 (same year as Maine) and rolled out retail more quickly, with first sales November 2018 (vs Maine's October 2020). However, Massachusetts implemented a high-tax structure that creates opportunity for Maine:
Massachusetts Tax Burden:
- State excise tax: 10.75%
- State sales tax: 6.25%
- Local option tax: Up to 3%
- Total burden: 20-27%
Result: Massachusetts pricing runs 25-40% higher than Maine for comparable products. Southern Maine dispensaries capture Massachusetts overflow—particularly from Greater Boston suburbs and New Hampshire border communities (Salem, Nashua, Manchester) where residents can reach Maine as easily as Massachusetts retail.
Vermont Limited Competition:
Vermont legalized adult-use sales later (2022) and maintains smaller retail footprint (~40 dispensaries for 645,000 residents). Western Maine faces potential competition from Vermont expansion, but currently Vermont's limited infrastructure and comparable pricing leave Maine's western border region underserved—opportunity rather than threat.
Tourism Amplification
Maine attracts 10 million tourists annually (May-August peak season), mostly passing through or starting from New Hampshire/Massachusetts. Border dispensaries report customers from Texas, Florida, New York, and Quebec—tourists stock up on cannabis unavailable or expensive in home jurisdictions.
Tourism + New Hampshire prohibition + Massachusetts high prices = powerful revenue generator for southern Maine's cannabis sector.
However, tourism creates seasonal volatility. Winter months see reduced traffic and sales, forcing dispensaries to maintain infrastructure costs during slow periods. This reduces profitability and creates pricing pressure that may disadvantage Maine vs year-round tourist destinations like Nevada.
The Interstate Commerce Irony
Maine profits from cannabis federalism's absurdity: A New Hampshire resident drives 20 minutes to Eliot, Maine, purchases 2.5 oz legally under Maine law, pays Maine taxes, then commits federal felony by transporting across state line. Maine collects revenue. New Hampshire criminalizes possession. Federal government ignores interstate trafficking unless distribution-scale.
This system benefits Maine fiscally but creates policy incoherence. Only federal legalization resolves interstate conflict—allowing legitimate commerce while focusing enforcement on unlicensed operations regardless of state boundaries.
The Enforcement Crisis: Chinese Organized Crime Infiltration
While Maine succeeds at retail legalization, the state faces unprecedented organized crime infiltration. Law enforcement estimates 100-200 illegal cultivation operations operate statewide, overwhelmingly linked to Chinese organized crime networks.
Scale of the Problem
Since June 2023:
- 60+ grow house raids conducted
- 25,000+ plants seized (Somerset County alone)
- 600+ pounds processed cannabis confiscated
- 30+ arrests made
- Zero convictions secured
Somerset County Sheriff Dale Lancaster: His 50,000-population county conducted nearly half of all raids statewide, straining resources to breaking point. "We have the intelligence to do this, but we don't have the resources."
The Criminal Enterprise Model
Organized crime networks exploit Maine's medical caregiver program:
- Property Acquisition: Purchase rural properties through shell companies using cash or complex financing
- License Gaming: Obtain medical caregiver licenses using fraudulent addresses/identities
- Mass Cultivation: Grow 150-2,600 plants per site (far exceeding medical limits)
- Labor Trafficking: Import Chinese nationals, house on-site, pay $1,000/month for 24/7 labor—indentured servitude
- Banned Pesticides: Use Eagle 20EW (creates hydrogen cyanide when combusted) and chlorfenapyr to maximize yields
- Distribution: Ship to unlicensed dispensaries in New York, California, Massachusetts; sell wholesale to Maine medical dispensaries at below-market rates
Public Health Crisis: 42% Contamination Rate
Studies in 2023 found 42% of Maine medical cannabis contaminated with pesticides, chemicals, or mold. Eagle 20EW (myclobutanil) was most commonly detected—a fungicide that creates hydrogen cyanide gas when combusted and inhaled.
October 2025 Recall: Maine's Office of Cannabis Policy issued recall for products containing chlorfenapyr, another banned pesticide linked to Chinese grow operations. Affected multiple dispensary chains: Cannabis Cured, Cannabis Haven, GreenLife, Belvidere Farm, Garden Lites, Hive LLC, OMG Cannabis Co.
Health Risks:
- Inhaling unsafe chlorfenapyr levels: High fever, sweating, nausea, vomiting, altered mental status
- Long-term Eagle 20EW exposure: Potential neurological damage from hydrogen cyanide
Consumer Trust Impact: Contamination scandals undermine legal cannabis's safety advantage over illicit market—one of framework's five critical policy levers. If legal dispensaries cannot guarantee product safety, consumers have reduced incentive to choose licensed sources.
Why Enforcement Fails
Resource Mismatch: County sheriffs with 10-30 deputies cannot combat transnational organized crime networks spanning China, California, New York, and Maine.
Federal Attention Gap: DEA, FBI, and Homeland Security provide raid assistance but lack resources for comprehensive Maine focus. Cannabis ranks lower priority than fentanyl despite organized crime links.
Prosecution Gaps: Despite 60 raids and 30+ arrests, zero convictions resulted. Complex federal/state jurisdictional questions, language barriers, and deportation as alternative to prosecution create "revolving door."
Regulatory Exploitation: Office of Cannabis Policy lacks statutory authority to deny medical caregiver licenses to convicted illicit cultivators. Individuals convicted of illegal cultivation can apply for license a month later.
Market Impact: Framework analysis suggests this enforcement failure reduces legal market share by 8-12 percentage points relative to optimized scenario. Without organized crime infiltration, Maine could achieve 72-78% legal share. Current estimate: 58-65% legal share.
The Medical Testing Crisis: LD 104 and LD 1847
Maine faces a unique medical cannabis problem: Maine is the ONLY U.S. state that doesn't require testing of medical cannabis for contaminants like pesticides, mold, and heavy metals. While adult-use cannabis must pass comprehensive testing, medical cannabis—supposedly for vulnerable patients—faces no such requirements.
LD 104: Mandatory Medical Testing (Carried Over to 2026)
Status: Bill carried over from 2025 session, will be reconsidered in 2026
Sponsor: Rep. Marc Malon (D-Biddeford), supported by Office of Cannabis Policy
Key Provisions:
- Require seed-to-sale tracking for medical cannabis (currently exempt)
- Mandate testing for pesticides, mold, heavy metals, contaminants for all medical cannabis
- Align medical testing standards with adult-use requirements
- Update adult-use testing requirements to reflect streamlined medical program standards
The Crisis LD 104 Addresses:
A 2023 Office of Cannabis Policy study found 42% of medical cannabis tested would have failed adult-use standards. Most common contaminant: Eagle 20EW (myclobutanil)—fungicide creating hydrogen cyanide when combusted.
Only two states nationally lack medical testing: Maine and Arkansas. Only three states lack seed-to-sale tracking: Maine, Missouri, and New Hampshire.
Maine's medical cannabis program has operated since 1999, when voters approved physician recommendations for therapeutic use, though implementation didn't occur until 2009 with licensing and regulation of caregivers and dispensaries. Despite 25+ years of medical legality, Maine remains the only state without mandatory testing for medical cannabis—a stunning regulatory gap that Chinese organized crime has exploited systematically.
Industry Opposition:
Maine Cannabis Union (industry advocacy group) opposes LD 104, arguing:
- Existing adult-use testing regime is "seriously flawed, overly burdensome, expensive"
- Recent product recalls demonstrate testing doesn't "effectively protect consumers"
- Small medical caregivers (1,600+ statewide serving 100,000+ patients) operate on thin margins
- Mandatory testing would add tens of thousands in annual costs, forcing many caregivers to exit
- "If either bill passed as written, the medical program would be done"
Public Health Advocates Support:
Maine Public Health Association argues:
- Medical cannabis patients managing health conditions "deserve assurance products aren't contaminated"
- 42% contamination rate is unacceptable for medicine
- Adult-use requires testing; medical patients deserve equal protection
CBDT Analysis:
LD 104 impacts the safety/quality variable (1.2× weight in framework). Implementing comprehensive testing would:
Positive Effects:
- Improve consumer confidence in legal market safety advantage (+3-5 percentage points legal share)
- Prevent contaminated cannabis from entering legal supply chains
- Reduce public health risks (cyanide exposure, pesticide poisoning)
Negative Effects:
- Small caregiver exits could reduce medical supply/access (-2-3 percentage points medical share)
- Testing costs could increase medical prices, driving some patients to illicit markets
- If not paired with enforcement against Chinese grow operations, testing alone won't solve contamination source
Net Impact: +1-3 percentage points legal market share IF implemented with enforcement investment and testing cost subsidies for small caregivers.
LD 1847: Testing + THC Potency Caps (Carried Over to 2026)
Status: Carried over from 2025 session alongside LD 104
Sponsor: Rep. Anne Graham (D-North Yarmouth)
Additional Provisions Beyond LD 104:
- THC potency caps on medical edibles (specific limits TBD)
- Study group examining youth cannabis use
- Divert adult-use tax revenue to public health/safety awareness
- Change packaging requirements for gummies to reduce accidental pediatric ingestion
The Pediatric Concern:
Testimony before Legislature highlighted children unintentionally ingesting high-THC hemp candies and sodas resembling regular snacks. Products in Maine stores offered 100mg+ total THC per package with minimal warnings. Packaging mimicked popular candy brands.
Industry Opposition:
Even stronger opposition to LD 1847 than LD 104 due to THC potency caps. Medical cannabis patients using high-THC products for chronic pain, PTSD, epilepsy argue caps would limit therapeutic efficacy.
CBDT Analysis:
Potency caps have mixed market impact:
- Positive: Reduce youth access concerns, improve public perception of responsible regulation
- Negative: Drive patients needing high-potency to illicit markets or home cultivation
- Net: Minimal impact on total legal share (±1-2 points) but significant impact on specific patient subpopulations
Why Both Bills Stalled:
Committee received ~1,000 pieces of written testimony criticizing Maine's cannabis testing program and questioning state standards. Industry unified in opposition. Public health advocates outnumbered by cannabis industry representatives. Political will insufficient in 2025 session.
Reconsideration Timeline: Both bills return in 2026 session. Office of Cannabis Policy Director John Hudak made clear implementing testing program is "top priority." Legislature will face same debate: patient safety vs. small business viability.
The June 2025 Tax Legislation: Policy Failure in Real Time
In June 2025, Maine's legislature passed legislation increasing adult-use cannabis sales tax from 10% to 14%—a 40% tax hike with an effective date of January 1, 2026—to address a $450 million state budget deficit. This decision demonstrates how fiscal crisis tempts policymakers to sacrifice long-term market optimization for short-term revenue.
The Fiscal Pressure
Maine faced $450 million projected deficit over 2025-2027 biennium. Adult-use cannabis tax revenue ($27.8M in 2024) represented tempting target for increase. Legislature calculated 40% tax increase would generate additional $11M annually starting in 2026.
The Trade-Off:
Short-term: +$11M annual revenue from tax increase (2026 forward)
Long-term: -6-8 percentage points legal market share = -$25-35M annual transaction volume flowing to illicit markets
Net Effect: State gains $11M in taxes but loses $14-24M in economic activity, plus enforcement costs pursuing illicit market growth.
CBDT Framework Analysis
Price competitiveness is 4× weighted variable in framework—most critical determinant of legal market success.
Tax Increase Impact:
Current (through December 31, 2025):
- Total tax burden: 18-20% (10% sales + 8-10% cultivator excise)
- Legal market share: 65-70% estimated
Post-January 1, 2026:
- Total tax burden: 24-26% (14% sales + 10% cultivator excise)
- Legal market share: 58-65% estimated
- Projected Decline: 5-7 percentage points
Consumer Behavior:
Research shows cannabis consumers highly price-sensitive—10% legal price increase reduces legal market choice probability by 2.3%. A 4-percentage-point tax increase (40% of previous 10% rate) translates to roughly 4% retail price increase, reducing legal market probability by ~1% directly, with additional effects from consumer perception and comparison to pre-tax pricing memory.
Illicit Market Response:
Chinese organized crime operations don't pay taxes. As legal prices increase 4% in January 2026, illicit operations will maintain pricing, widening price gap and recapturing market share lost since 2020.
Comparison to Other Markets
Cautionary Examples:
Washington State: Implemented 37% excise tax, achieving only 60-65% legal share despite early-mover advantage
Illinois: Combined state/local taxes reaching 25-40%, achieving only 50-55% legal share
California: Tax stacking (cultivation + excise + sales + local) reaching 45%+ in some jurisdictions, achieving only 50% legal share
Success Examples:
Colorado: Maintained 15% excise + ~8% sales = 23% total burden, achieving 84-88% legal share
Michigan: 10% excise + 6% sales = 16% total burden, achieving 85% legal share
Missouri: 6% excise + local option ≤3% = 9-12% total burden, achieving 62-68% legal share
Pattern: States maintaining total tax burden under 20-22% outperform high-tax states by 15-35 percentage points legal share.
Maine's Position: At 24-26% total burden, Maine now sits in the "struggling" category alongside Washington and Illinois rather than "successful" category with Colorado and Michigan.
The Revenue Optimization Paradox
Fiscal logic: Higher tax rate × same transaction base = more revenue
Market reality: Higher tax rate → lower transaction base → comparable or less revenue + stronger illicit market
Example:
Scenario A (10% tax rate, 65% legal share):
- Total market: $380M
- Legal transactions: $247M (65%)
- Tax revenue: $24.7M
Scenario B (14% tax rate, 60% legal share):
- Total market: $380M
- Legal transactions: $228M (60%)
- Tax revenue: $31.9M
Short-term: Scenario B generates +$7.2M revenue
Long-term: Scenario B's lower legal share means:
- $19M additional illicit market activity
- Reduced legitimate employment
- Increased enforcement costs
- Reduced consumer safety (untested products)
- Harder to recapture market share once consumers habituate to illicit sources
Optimal Strategy: Maintain 18-20% tax burden, invest enforcement to grow legal share to 72-78%, generating:
- Total market: $400M
- Legal transactions: $300M (75%)
- Tax revenue @ 18%: $54M
Revenue maximization comes through volume (market share) not rates.
Predicted Market Trajectories
Current Performance: 65-70% Legal Market Share (November 2025, Pre-Tax Increase)
Framework Inputs (Current State):
- Price Competitiveness: Currently competitive at 18-20% total burden. Will worsen significantly January 1, 2026 when 14% sales tax takes effect (24-26% total burden).
- Access Density: Strong in southern Maine (16% municipal opt-in), severe fragmentation in rural areas
- Safety/Quality: Compromised by medical contamination (42% failure rate). Consumer confidence weakened.
- Convenience: Cash-only operations create friction. No statewide delivery mandate.
- Enforcement: Critical failure. 100-200 organized crime operations, zero convictions despite 60 raids.
Current Legal Share: 65-70% (through December 2025)
Post-Tax Increase Projection: 58-65% (starting January 2026)
Comparable Performance:
- Similar to Washington: 60-65%
- Below Michigan: 85%
- Below Colorado: 84-88%
- Above California: 50%
Scenario 1: Policy-Corrected Optimization (72-78% Legal Share)
Required Changes:
State Actions:
- Repeal or delay the 14% sales tax (reverse June 2025 legislation before January 1, 2026 effective date)
- If repeal impossible, reduce from 14% back to 10-12% to minimize damage
- $18-25M annual enforcement budget targeting organized crime
- Close licensing loopholes (deny licenses to convicted operators for 5 years)
- Implement LD 104 with small caregiver subsidies (testing requirements + cost assistance)
- Revenue sharing with municipalities (5% of sales tax to hosting towns)
- Statewide delivery mandate for areas >10 miles from dispensary
Federal Reform:
- Schedule III rescheduling (eliminates 280E tax burden)
- SAFE Banking Act passage (enables card payments)
- Federal enforcement cooperation (sustained DEA/FBI presence)
Predicted Outcomes:
- Transaction share: 72-78%
- Volume share: 60-68%
- Timeline: 36-48 months post-policy implementation
- Comparable to: Michigan current performance
Economic Impact:
- Legal market: $380-420M annually (mature market)
- State tax revenue: $68-76M annually (at 18-20% burden)
- Jobs: 4,500-5,500 direct + indirect
- Illicit market: Reduced to $90-140M (18-25% of total demand)
Scenario 2: Tax Increase Takes Effect, Limited Reforms (58-65% Legal Share)
Policy Reality:
- 14% sales tax takes effect January 1, 2026 as scheduled
- Limited enforcement improvements (insufficient resources)
- Medical testing bills stall again in 2026
- Municipal fragmentation persists
- Federal reform delayed
Predicted Outcomes:
- Transaction share: 58-65% (starting January 2026)
- Volume share: 45-52%
- Timeline: 2026-2028 steady state
Economic Impact:
- Legal market: $240-280M annually
- State tax revenue: $34-39M annually (at 24-26% burden)
- Jobs: 3,200-3,800
- Illicit market: $120-180M (35-42% of total demand)
Consequences:
- Chinese organized crime maintains operations
- Contaminated cannabis continues entering medical supply
- New Hampshire border advantage partially lost as residents find Massachusetts more competitive
- Maine falls further behind Michigan and Colorado
Scenario 3: Worst Case—Further Tax Increases (45-55% Legal Share)
Policy Failure:
- 14% tax takes effect January 2026, THEN increased further (to 16-18%) due to continued budget deficits
- Enforcement deprioritized (budget cuts)
- LD 104 rejected permanently
- Municipal opt-outs increase
- Federal reform stalls indefinitely
Predicted Outcomes:
- Transaction share: 45-55%
- Volume share: 32-42%
- Timeline: 2027-2029
- Comparable to: California (50%), Illinois (50-55%)
Economic Impact:
- Legal market: $180-240M annually
- State tax revenue: $32-43M annually (high rate on small base—potentially LESS than current $27.8M at 10%)
- Jobs: 2,400-3,200
- Illicit market: $160-240M (40-55% of total demand)—majority control
This represents policy catastrophe: Maine legalizes cannabis but fails to achieve public safety goals (black market reduction), loses competitive advantage to Massachusetts and Vermont, and generates disappointing revenue despite high tax rates.
Federal Policy Barriers
Maine cannot optimize alone. Federal prohibition creates structural barriers preventing state-level success.
The 280E Problem
Internal Revenue Code Section 280E prohibits cannabis businesses from deducting ordinary expenses (rent, salaries, utilities), creating effective federal tax rates of 40-70%.
Impact: Maine dispensaries must raise prices 15-20% above economic efficiency just to survive federal tax burden. This artificially reduces price competitiveness, enabling organized crime to undercut legal retailers.
Solution: Schedule III rescheduling eliminates 280E. Retail prices drop 12-18%, improving competitiveness. Estimated impact: +6-10 percentage points legal market share.
The SAFE Banking Problem
Without SAFE Banking Act passage, Maine dispensaries operate cash-only, creating:
- Security costs: $70,000-150,000 annually per location
- Consumer friction: Reduces transaction frequency 18-25%
- Crime risk: Cash-heavy businesses become robbery targets
Solution: SAFE Banking enables normal banking access and card payments. Estimated impact: +5-8 percentage points legal market share.
The Enforcement Coordination Problem
County sheriffs cannot investigate transnational money laundering networks. Chinese organized crime requires federal response that state/local law enforcement cannot provide.
Solution: Federal legalization or Schedule III + interstate commerce framework enables proper federal/state/local task forces with sustained funding.
Policy Recommendations
For Maine Legislature
URGENT Priority: Prevent Tax Increase Disaster
Maine's legislature has until December 31, 2025 to prevent the 14% sales tax from taking effect. The June 2025 legislation can be amended or repealed before the January 1, 2026 effective date.
Options:
- Repeal the increase entirely—maintain 10% sales tax rate
- Reduce to 11-12%—compromise that minimizes damage while generating modest additional revenue
- Delay effective date—postpone to 2027 or later, allowing market to stabilize and enforcement to improve before tax increase
- Tie to enforcement funding—make tax increase contingent on $18-25M annual enforcement appropriation, ensuring revenue supports optimization
Economic Case: Tax increase will reduce legal market share 6-8 percentage points, costing $25-35M in lost economic activity while generating only $11M additional revenue. Net loss to state economy: $14-24M annually.
Priority #2: Enforcement Investment
- $18-25M annual budget for cannabis-specific illicit cultivation interdiction
- Multi-agency task force (State Police, OCP enforcement, county sheriffs, federal partners)
- Focus on large-scale operations (100+ plants), organized crime networks
Priority #3: Implement LD 104 with Support
- Pass mandatory medical testing with testing cost subsidies for small caregivers
- Differentiate: personal caregivers (<30 plants) maintain flexibility, commercial-scale (100+ plants) face testing requirements
- Pair testing mandate with enforcement against contamination sources (Chinese grow operations)
Priority #4: Municipal Access Expansion
- 5% revenue sharing with municipalities hosting dispensaries
- Statewide delivery mandate for areas >10 miles from retail
- Reduce barriers to municipal opt-in (currently 16% participation)
For Office of Cannabis Policy
- Expand enforcement division from 8-10 FTE to 30-40 dedicated investigators
- Establish intelligence-sharing partnerships with DEA, FBI, Homeland Security
- Develop database tracking raided properties, convicted operators, shell companies
- Publish quarterly enforcement reports (transparency builds public trust)
For Congressional Delegation
Senators Susan Collins (R) and Angus King (I), Representatives Chellie Pingree (D) and Jared Golden (D):
- Co-sponsor and advocate for SAFE Banking Act—eliminates cash-only operations
- Support Schedule III rescheduling—eliminates 280E burden
- Request sustained federal task force presence—Maine needs DEA/FBI resources to combat Chinese organized crime
Comparison to Other Markets
High Performers (80%+ Legal Share):
- Michigan: 85% (competitive pricing, strong enforcement, no local bans)
- Colorado: 84-88% (mature market, moderate taxes)
- Nevada: 75-80% (tourism amplification)
Mid-Tier (60-75%):
- Oregon: 95% transaction, 82% volume (lowest prices nationally)
- Washington: 60-65% (high taxes limit performance)
- Maine Current: 58-65% (post-tax increase, enforcement failure)
Struggling (30-60%):
- Illinois: 50-55% (very high taxes)
- California: 50% (fragmentation + high taxes)
- New York: 30% (regulatory collapse)
Maine's Position: Currently mid-tier but trending toward "struggling" category due to June 2025 tax increase. Policy correction could restore top-quartile performance; continued tax pressure risks California-level dysfunction.
Timeline and Economic Reality
Current State (2024-2025)
Legal Market: $244M adult-use + $40-50M medical = $284-294M total
Tax Revenue: $30-31M annually (increasing to ~$34M at 14% rate but on smaller base)
Employment: 3,600-4,200 jobs (direct + ancillary)
Illicit Market: $120-180M (35-42% of consumption)
Optimized State (2029-2030 with Policy Corrections)
Legal Market: $380-420M annually
Tax Revenue: $68-76M annually (at 18-20% burden)
Employment: 6,000-7,500 jobs
Illicit Market: Reduced to $90-140M (18-25%)
Net Gain: +$38-45M annual tax revenue, +2,400-3,300 jobs, -48-65% illicit market reduction
Conclusion
Maine's cannabis market stands at a critical crossroads. The state succeeds at retail infrastructure—170+ dispensaries serving residents and capturing substantial New Hampshire cross-border traffic at competitive prices. Yet Maine simultaneously battles organized crime infiltration at scale, with Chinese criminal networks operating 100-200 grow houses producing contaminated cannabis that corrupts medical supply chains and consumer confidence.
Most urgently, Maine's legislature has until December 31, 2025, to prevent a policy disaster. The June 2025 tax legislation increasing adult-use sales tax from 10% to 14% takes effect January 1, 2026. This single decision will reduce legal market share by 6-8 percentage points, undermining years of progress just as enforcement crisis peaks. There is still time to repeal, reduce, or delay this tax increase.
Maine's path to optimization requires:
State level (Time-Sensitive):
- Repeal or delay 14% tax increase before January 1, 2026 (URGENT)
- Enforcement investment ($18-25M annually)
- Implement LD 104 testing with caregiver support
- Municipal access expansion (revenue sharing, delivery mandate)
Federal level:
- Schedule III rescheduling (eliminates 280E)
- SAFE Banking (enables normal operations)
- Enforcement coordination (federal resources against organized crime)
Without policy corrections, Maine declines from current 65-70% legal share to 58-65% (January 2026) and potentially 45-55% if further tax increases follow. With corrections and federal reform, Maine reaches 72-78%—top-quartile performance matching Michigan and approaching Colorado.
The economic stakes: +$38-45M annual tax revenue (optimized) versus -$14-24M net economic loss (tax increase as scheduled). The public health imperative: 42% medical cannabis contamination endangers patients. The enforcement necessity: transnational organized crime cannot operate with impunity.
Maine has structural advantages—border position, competitive pricing, strong retail density, tourism amplification. Policy reforms are achievable. The next five weeks determine Maine's trajectory for the next five years. Will Maine's legislature prevent the January 2026 tax disaster, invest in enforcement, and implement comprehensive testing? Or will the state sacrifice optimization for short-term budget relief while organized crime flourishes?
The framework suggests the choice is clear. Maine's voters approved legalization in 2016 via Question 1. Now the state must implement it effectively—starting with preventing the scheduled tax increase from taking effect in 35 days.
CBDT Framework Citation
This analysis applies the Consumer-Driven Black Market Displacement Framework:
The Silent Majority 420, "Consumer-Driven Black Market Displacement (CBDT) Framework: A Behavioral-Utility Heuristic for Illicit-to-Legal Market Transition," Zenodo, 2025. DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.17593077
Validation data: Harvard Dataverse, DOI: 10.7910/DVN/MDVDTQ
Related State Analyses: Rhode Island | New Mexico | S Dakota | N Carolina
The Silent Majority 420 is an independent cannabis policy analyst. The CBDT Framework represents the first validated consumer-utility model for predicting market outcomes in vice legalization.
Analysis licensed CC BY 4.0
