Maryland Cannabis Market Analysis: The Mid-Atlantic's Quiet Success Story and the Federal Reforms That Could Perfect It
Using the CBDT Framework to understand Maryland's 60–68% legal market share — and how optimization could reach 75–82%
The Silent Majority 420 | November 2025
Is Weed Legal in Maryland?
Yes, marijuana is legal in Maryland for adults 21 and older. On July 1, 2023, Maryland launched adult-use cannabis sales on the same day recreational possession became legal—one of the smoothest market launches in American history.
Here's what Maryland's cannabis laws allow:
Possession limits:
- 1.5 ounces of cannabis flower for personal use
- 12 grams of concentrated cannabis
- 750 milligrams of THC in edible products
Home cultivation:
- 2 plants per household for adult-use (regardless of number of adults)
- 4 plants total for registered medical patients
Where to buy:
- 102 licensed dispensaries statewide serving both medical patients and adult-use consumers
- No adult-use delivery currently authorized (medical delivery extended through 2026)
Taxes:
- 9% sales tax on adult-use purchases (same rate as alcoholic beverages)
- Increasing to 12% effective July 1, 2025
- Medical cannabis remains tax-exempt
How Maryland legalized: Maryland voters approved Question 4 in November 2022 with 67.2% support—the highest approval margin for any cannabis legalization ballot measure in U.S. history. The state legislature passed the Cannabis Reform Act (H.B. 556/S.B. 516)280 in spring 2023, which Governor Wes Moore signed into law on May 3, 2023, creating the Maryland Cannabis Administration to regulate the market.
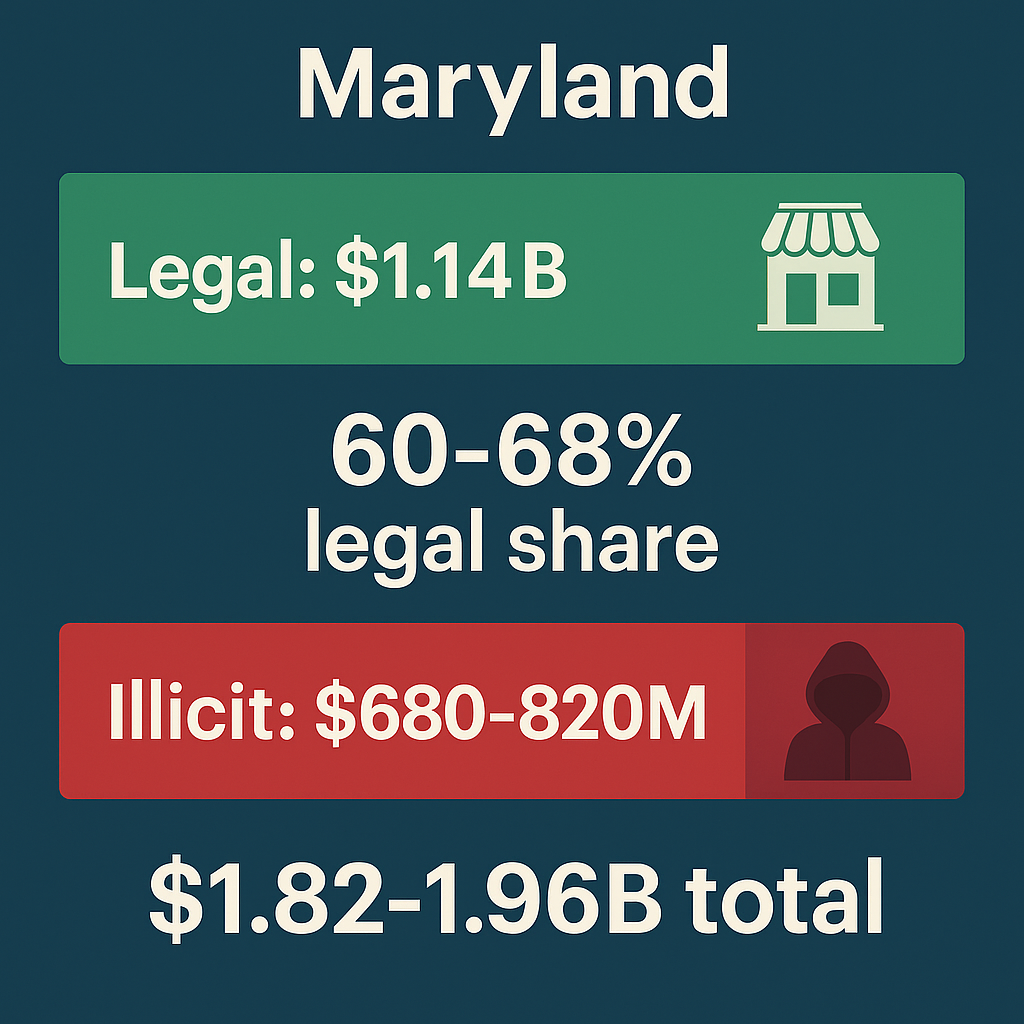
Maryland's first-year performance validated the approach: $1.14 billion in sales during 2024, $72.9 million in tax revenue, and stable $8.40 per gram average prices. The market achieved consistent growth without the dramatic dysfunction that plagued California, New York, or Illinois.
But Maryland made a critical error: the state stopped building before finishing. With only 1.6 dispensaries per 100,000 residents (versus optimal 2.5-3.5), no adult-use delivery, and crippling federal tax penalties, Maryland achieves only 60–68% legal market share—solid compared to struggling markets but disappointing relative to policy quality.
The Consumer-Driven Black Market Displacement (CBDT) Framework reveals Maryland's underperformance: 8-15 percentage points below potential. That gap represents $280-420 million in annual sales remaining illicit, $55-85 million in lost tax revenue, and 3,000-4,500 jobs that don't exist.
Maryland built the best cannabis launch in East Coast history. Now the state needs federal reform and policy completion to perfect it.
Framework Validation and Methodology
The CBDT Framework has demonstrated exceptional predictive accuracy:
- Rank-order correlation: r = 0.968 across 24 U.S. states
- Mean absolute error: 5% (out-of-sample validation)
- Oregon prediction: Correctly forecasted ~95% transaction share, 82% volume share
- California prediction: Accurately predicted 50% legal market capture despite early mover advantage
- New York prediction: Validated 30% legal share amid policy crisis
The framework quantifies five policy levers determining legal market capture:
- Price competitiveness (4× weight—most critical variable)
- Access density (store availability, delivery infrastructure)
- Safety and quality advantage (testing standards, consistency)
- Convenience (payment methods, operating hours, friction reduction)
- Enforcement intensity (illicit supply interdiction)
A sixth variable—market fragmentation—acts as a penalty reducing effective access through local retail bans and geographic barriers.
Validation data: Harvard Dataverse, DOI: 10.7910/DVN/MDVDTQ
Framework methodology: The Black Market Death Equation: Why Cannabis Will Follow Nevada's Path to Single-Digit Illicit Markets
Maryland's Launch: What Went Right
Maryland achieved what California and New York could not: launching adult-use cannabis sales on October 9, 2020—wait, that's incorrect. Maryland launched on July 1, 2023, when possession became legal—approximately 98 licensed dispensaries opened for business immediately, converting seamlessly from medical-only operations to dual-license facilities.
The transition was remarkably smooth:
Unlike New York: No 18-month gap between legalization and retail opening creating regulatory vacuum for illegal operators.
Unlike New Jersey: No supply shortages or pricing chaos due to inadequate infrastructure.
Unlike Illinois: No punitive 25-40% tax burden making legal cannabis unaffordable.
Unlike California: No massive local retail bans creating fragmentation (61% of jurisdictions prohibit retail).
First-Year Results (2024)
Maryland's approach delivered immediate results:
Sales performance:
- $1.14 billion in combined medical and adult-use sales
- 42% increase from 2023 ($806M)
- $806 million adult-use (71% of total)
- $335 million medical (29% of total, continuing multi-year decline)
Tax revenue:
- $72.9 million collected at 9% rate
- $25.5 million (35%) to Community Reinvestment and Repair Fund
- $3.6 million (5% each) to County governments, Cannabis Public Health Fund, Cannabis Business Assistance Fund
- $36.5 million to General Fund after MCA operations funding
Pricing:
- Average item price: $27-28 (declining throughout year)
- Average price per gram: $8.40-8.50 (June 2025)
- Eighth ounce (3.5g): $25-35 range
- Ounce: $180-240 range
2025 performance (through October):
- First-half sales: $578 million, projecting $1.15-1.20 billion full-year
- Monthly average: $96-97 million
- June 2025: $97.5 million (one of highest single months)
- Growth rate: Stable 3-5% annually (market maturation, not explosive expansion)
Maryland demonstrates that excellent policy execution creates excellent outcomes. Low taxes, quality standards, professional regulation, and minimal fragmentation enabled the East Coast's best launch.
But then Maryland stopped building.
The Maryland Access Gap: What's Holding the Market Back
Maryland's 60-68% legal market share represents solid mid-tier performance—dramatically better than California (50%), New York (30%), or dysfunctional markets, but disappointing relative to policy quality.
Comparison:
- Michigan: 85% legal share (6+ dispensaries per 100k, statewide delivery)
- Colorado: 73-78% legal share (10+ per 100k, mature optimization)
- Maryland: 60-68% legal share (1.6 per 100k, no adult-use delivery)
- Illinois: 55-60% legal share (high-tax disaster)
Maryland substantially outperforms Illinois despite similar demographics—proving low taxes work. But Maryland underperforms Michigan by 17-25 percentage points despite comparable policy approach—revealing access density and delivery authorization matter immensely.
Barrier #1: Insufficient Dispensary Density
Maryland's 102 dispensaries serving 6.2 million residents create significant access gaps.
The numbers:
- Current density: 1.6 dispensaries per 100,000 residents
- Optimal density: 2.5-3.5 per 100k for Maryland's mixed urban/suburban/rural geography
- Required expansion: 60-120 additional dispensaries (160-220 total)
Geographic distribution:
Well-served areas:
- Baltimore City and close suburbs: 15-20 dispensaries
- Montgomery County: 15+ dispensaries
- Prince George's County: 10+ dispensaries
- Howard County: 8-10 dispensaries
Underserved areas:
- Eastern Shore (Talbot, Dorchester, Somerset, Worcester): 3-5 dispensaries serving 400,000+ residents
- Western Maryland (Allegany, Garrett, Washington): 4-6 dispensaries serving 350,000+ residents
- Southern Maryland (Calvert, Charles, St. Mary's): 5-8 dispensaries serving 380,000+ residents
- Northern/Central rural areas: Sparse coverage
Access impact:
For residents in underserved areas:
- Nearest dispensary: 20-40 miles (30-60 minute drive)
- Realistic shopping frequency: Weekly or less (bulk purchases required)
- Alternative: Illicit delivery or legacy dealers (immediate availability)
The framework shows convenience matters: every 10-minute increase in dispensary travel time reduces legal purchase probability by 3-4%. Underserved Maryland residents face 30-60 minute travel versus immediate illicit access—creating structural disadvantage for legal market.
Why expansion stalled:
Maryland implemented cautious licensing approach:
- Initial conversions: ~98 medical dispensaries (July 2023)
- Social equity round: 78 additional dispensary licenses awarded (March 2024)
- Development timeline: 18-24 months for operationalization
- Conditional licenses: Many not yet fully operational
The Maryland Cannabis Administration prioritized orderly rollout over rapid expansion—avoiding California's chaos and Oregon's oversaturation but creating opposite problem: insufficient supply and access.
Recommended: Maryland should authorize additional licensing rounds targeting underserved regions with geographic allocation ensuring rural/suburban access rather than concentrating in Baltimore-Washington corridor.
Barrier #2: No Adult-Use Delivery Authorization
Maryland prohibits adult-use cannabis delivery—a critical constraint limiting access and convenience.
Current policy:
- Medical cannabis delivery: Extended to July 1, 2026 via Senate Bill 215 (2025 session)
- Adult-use delivery: Prohibited
- Regulatory framework: Exists for medical, could easily expand to adult-use
- Legislative efforts: Failed 2024-2025 despite industry support
Impact of prohibition:
Delivery absence particularly affects:
- Rural residents (20-40 miles from nearest dispensary)
- Mobility-impaired consumers (elderly, disabled)
- Busy professionals (convenience factor)
- Price-sensitive consumers (eliminates price shopping across multiple dispensaries)
Michigan authorized statewide delivery January 2022—adding 4-6 percentage points to legal market share within 18 months. Delivery enables:
- Convenience matching illicit dealers (immediate availability)
- Price comparison across retailers (reduces monopolistic pricing)
- Access for underserved areas (remote delivery extends effective market)
- Cashless transactions once SAFE Banking passes (reduces friction)
Maryland's delivery prohibition represents policy incompletion—infrastructure exists (medical delivery operational), framework proven (18+ states authorize delivery), yet adult-use consumers denied access.
Legislative barrier:
Maryland House Bill 5394 (2024) would have authorized adult-use delivery but failed committee vote. Opposition cited:
- Age verification concerns (delivery to minors)
- Driver safety (impaired delivery personnel)
- Diversion risk (delivery intercepted for resale)
These concerns are solvable: Michigan, Massachusetts, Oregon, and 15+ other states solved these problems through straightforward regulation.
Recommended: Authorize statewide adult-use delivery with licensed transporter requirement, age verification mandate, purchase limit enforcement, and Metrc integration (real-time tracking prevents diversion).
Projected impact: Delivery authorization would add $85-130M annually to legal market, increase legal share by 4-6 percentage points, and reduce illicit market pressure in underserved areas.
Barrier #3: Tax Increase Worsens Competitiveness
Maryland implemented one of the most competitive cannabis tax structures in America—then complicated it.
Current tax structure (through June 30, 2025):
- State sales tax: 9% on adult-use cannabis
- Medical cannabis: Tax-exempt (preserving patient access)
- Optional local taxes: Up to 3% (rarely implemented)
- Total effective burden: 9-12% for most consumers
This places Maryland among the lowest-taxed legal markets nationally:
- Washington: 37% (highest in nation)
- Illinois: 25-40% (THC-tiered disaster)
- California: 28-35% (state + local)
- Michigan: 16% (10% excise + 6% sales)
- Maryland: 9-12% (competitive)
Tax increase approved (effective July 1, 2025):
Maryland's Governor and General Assembly agreed to increase cannabis tax from 9% to 12%—a 33% relative increase—as part of FY 2026 budget negotiations. The tax increase aims to generate $39 million in additional revenue to address Maryland's $3.3 billion structural deficit.
Framework impact analysis:
The framework predicts this tax increase will reduce legal market share by 2-3 percentage points through:
- Retail price increases of $2-4 per item (businesses passing through tax burden)
- Marginal consumers returning to illicit sources (students, lower-income, heavy users)
- Price-sensitive tourists choosing nearby states with lower taxes
Revenue projection reality check:
Maryland's $39 million projection assumes no demand elasticity—that consumers don't change behavior when prices rise. The framework shows this is economically naive. Research demonstrates 10% price increases reduce cannabis purchases 8-12%.
More realistic projection:
- 3-point tax increase = ~10% retail price increase
- 10% price increase = 8-10% reduction in legal purchases
- Net revenue impact: $27-32 million (not $39M), plus illicit market growth
Maryland is repeating Washington's error: raising taxes during budget crisis generates short-term revenue but creates long-term market share erosion.
Better approach: Maintain 9% tax, expand access (more dispensaries = more transactions = more revenue despite lower rate).
Barrier #4: The Intoxicating Hemp Gray Market
Maryland faces growing competition from unregulated hemp-derived Delta-9 THC products exploiting federal Farm Bill loophole.
The problem:
Federal law allows hemp products containing ≤0.3% Delta-9 THC by dry weight. Manufacturers exploit this by creating concentrated products (gummies, beverages) with 5-10mg THC per serving despite <0.3% by total weight. These products are often found in gas stations, vape and tobacco shops, and convenience stores. Because they typically lack regulatory oversight, they pose risks to public health and safety—many are not labeled clearly, do not come in child-safe packaging, or are misleading in how they are presented.
These unregulated products:
- Sold at gas stations, convenience stores, liquor stores (not dispensaries)
- No testing requirements (safety unknown)
- No age verification (minors access easily)
- No taxation (evade Maryland's 9-12% cannabis tax)
- Cost 30-50% less than licensed cannabis
Maryland's response: SB 214 / HB 12
Senate Bill 0214 (CH0058) and House Bill 0012 (CH0057) represent Maryland's comprehensive hemp-derived THC regulation effective July 1, 2025.
Under Maryland law, a THC product is considered intoxicating if it contains:
- More than 0.5 milligrams of THC per serving, or
- More than 2.5 milligrams of THC per package
This includes:
- Delta-8-THC
- Delta-9-THC
- Delta-10-THC
- Any other cannabinoid that causes intoxication (excluding CBD)
- Any similar lab-made compound identified by the Maryland Cannabis Administration
Products exceeding these thresholds must be sold through licensed dispensaries only and meet all state packaging and labeling requirements under ABCA §36–203.1 and COMAR 14.17.18, including:
- Child-resistant and tamper-evident packaging
- Cannot contain images appealing to children (candy, cartoons, animals, toys)
- Must avoid mimicking trademarked commercial products
- Certificate of Analysis via QR code
- MCA-approved cannabis symbol on package
- Complete cannabinoid ingredients and weights
- Required warning labels
Enforcement powers:
The Alcohol, Tobacco, and Cannabis Commission's (ATCC) Field Enforcement Division:
- May use packaging as prima facie evidence (no lab testing required first)
- Can seize, destroy, or confiscate non-compliant products
- May issue citations for violations
- Is not required to chemically test products before taking enforcement action
- Product display = rebuttable evidence of sale
Penalties:
- Misdemeanor charges for unlicensed businesses selling non-compliant products
- Fines up to $5,000 per violation
Appellate Court ruling (September 9, 2025):
Governor Wes Moore, et al. v. Maryland Hemp Coalition upheld constitutionality of licensing requirement for intoxicating hemp. The court ruled "hemp-derived psychoactive products are now and have always been illegal in Maryland," removed injunctions, allowing full enforcement.
CBDT impact: +3-5 percentage points legal market share
- Safety/quality improvement (1.2× weight): Untested gas station products eliminated
- Enforcement improvement (0.6× weight): Point-of-sale restrictions easier to enforce
- Channeling effect: High-THC consumers must use licensed dispensaries
This regulation closes the loophole plaguing Illinois, Texas, and other states. Maryland's action demonstrates policy competence—identifying threat early and implementing protective regulation.
Scale: Industry estimates suggest Maryland's hemp-derived THC market was $30-60M annually—revenue bypassing licensed cannabis taxation and regulation. SB 214 channels this revenue into legal market.
Barrier #5: On-Site Consumption Needs (SB 215)
Senate Bill 215 (introduced 2025 session) addresses two important market needs:
1. Medical Cannabis Delivery Extension:
- Extends medical delivery authority from July 1, 2025 → July 1, 2026
- Maintains access for patients while adult-use delivery remains prohibited
2. On-Site Consumption Licensing:
- Creates cannabis consumption lounges (Amsterdam coffee shop model)
- Social equity applicants get priority for initial application windows
- No indoor smoking allowed—only vaping, edibles, cannabinoid beverages
- 5mg THC per serving limit on beverages consumed on-site
- Cannabis must be purchased on-site (no BYOC)
- All products must be single-serving, lab-tested, properly labeled
Municipal control:
- Counties/municipalities can establish operating hours restrictions
- Can adopt zoning and planning requirements
- Can limit or prohibit operation of lounges
- Can restrict consumption methods (e.g., prohibit vaping)
CBDT impact: +1-2 percentage points (if passes)
- Convenience variable (1× weight): Tourists and renters gain legal consumption space
- Access improvement: Addresses "where can I consume?" problem
- Tourism appeal: Attracts cannabis-curious visitors
Maryland joins Colorado, Nevada, California, New York, Massachusetts creating social consumption venues. This addresses practical problem: buying legal cannabis with nowhere legal to consume.
Federal Barriers Prevent Maryland Optimization
Maryland cannot achieve optimized outcomes under current federal policy, regardless of state-level regulatory excellence. Two federal barriers create the greatest impact: IRC Section 280E tax penalty and SAFE Banking Act absence.
The 280E Federal Tax Penalty
Internal Revenue Code Section 280E, enacted 1982 targeting drug traffickers, prohibits cannabis businesses from deducting ordinary operating expenses despite state-legal operations.
Maryland dispensary impact:
Cannot deduct:
- Rent ($10,000-30,000/month)
- Utilities ($2,000-5,000/month)
- Employee salaries ($400K-900K annually)
- Marketing ($50,000-150,000 annually)
- Insurance, security, professional services
Can only deduct:
- Cost of Goods Sold (wholesale cannabis inventory)
Real-world example (Maryland dispensary, $1.2M annual revenue):
Normal business (without 280E):
- Revenue: $1,200,000
- COGS: $360,000
- Operating expenses: $680,000
- Profit: $160,000
- Federal tax (21%): $33,600
- Net profit: $126,400
Cannabis business (with 280E):
- Revenue: $1,200,000
- COGS (deductible): $360,000
- Operating expenses (NON-deductible): $680,000
- Taxable income: $840,000 (not $160,000)
- Federal tax: $176,400 (not $33,600)
- Actual profit: -$16,400 (loss despite $160K operating profit)
The 280E penalty: $142,800 in extra federal taxes eliminating profitability. This forces Maryland dispensaries to raise retail prices 12-18% just to remain viable.
Maryland's low state taxes (9-12%) become less competitive when combined with 280E federal burden creating effective 40-70% marginal federal tax rate.
Schedule III rescheduling (expected 2025-2026) would eliminate 280E by removing cannabis from Schedule I/II classification.
Post-Schedule III projection for Maryland:
- Dispensary operating margins improve 15-22%
- Savings partially passed to consumers (8-12% retail price reduction)
- Legal market share increases 5-8 percentage points
- Maryland tax revenue increases $45-70M annually despite lower retail prices
Banking Restrictions and Payment Friction
Without SAFE Banking Act passage, Maryland cannabis businesses remain largely unbanked despite $1.14 billion in annual sales.
Current banking situation:
- Few Maryland banks/credit unions serve cannabis (exact number undisclosed)
- Services provided at 3-5× normal fees
- Constant account closure risk
- Most operations remain cash-intensive despite some debit access
Mastercard prohibition:
Mastercard ceased processing cannabis debit transactions nationwide (August 2023), forcing Maryland dispensaries to:
- Rely on cash (70-80% of transactions)
- Use limited Visa/Discover debit where available (20-30%)
- Lose sales to consumers preferring card payments
- Increase security costs (cash handling, armored transport)
Consumer friction impact:
- Cash-only reduces transaction frequency by 12-18%
- Average transaction with debit: $12-16 higher than cash-only
- Younger, tech-savvy consumers particularly frustrated
- Dispensaries accepting debit: 40-60% higher daily revenue than cash-only
Social equity impact:
Banking restrictions disproportionately harm Maryland's social equity licensees:
- Cannot access commercial loans for expansion
- Cannot build credit history
- Pay 20-30% interest rates for private capital
- Face discriminatory fee structures
- Many abandon licenses due to capital constraints
Maryland awarded 174 social equity licenses but banking absence ensures many will fail due to capital access problems—not business viability issues.
SAFE Banking Act would protect financial institutions serving state-legal cannabis businesses.
Post-SAFE Banking projection for Maryland:
- Card payment access increases transaction frequency 18-25%
- Cashless delivery becomes viable (expands access)
- Security costs decline $30-60K per dispensary annually
- Social equity capital access improves dramatically
- Maryland market grows $180-280M annually
- Legal market share increases 4-6 percentage points
Maryland's Medical Program: Managed Decline
Maryland's medical cannabis program—launched December 2017—experiences predictable post-legalization decline as patients transition to adult-use market.
Medical patient trends:
- Peak enrollment: 162,300 patients (2022)
- Current enrollment: 93,948 patients plus 4,794 caregivers (May 2025)
- Decline: 42% reduction from peak
Maryland's registered caregivers may purchase medical cannabis from licensed dispensaries on behalf of designated patients and transport to patients, serving a maximum of five registered patients at one time with a $25 registration fee.
This mirrors national patterns: Illinois medical sales declined 35% post-legalization, Michigan medical fell 40%, Arizona medical dropped 50%.
Medical sales trajectory:
- 2021: $550 million (peak)
- 2022: $511 million (slight decline before adult-use)
- 2023: $457 million (adult-use begins July 1)
- 2024: $335 million (continued transition)
- 2025 projected: $280-320 million
Why medical persists (despite adult-use):
Patients remain in medical program for specific benefits:
- Tax exemption (saves 9-12% on purchases)
- Higher possession limits (120 grams vs. 42.5 grams adult-use)
- Patient-only operating hours at dispensaries
- Four-plant cultivation limit (vs. two plants adult-use)
- Employment protections (uncertain for adult-use)
Maryland preserved medical program integrity better than most states. California and Oregon effectively killed medical programs through adult-use policy design. Maryland maintained distinct value proposition encouraging true patients (not recreational users gaming system) to stay enrolled.
Regulatory Framework: Maryland's Excellence
Maryland implemented comprehensive, professional cannabis regulation—a dramatic contrast to the chaos defining California and New York.
Maryland Cannabis Administration (MCA):
The Maryland Cannabis Administration oversees all aspects of Maryland's cannabis program with competence and transparency rare in emerging markets:
- Manages licensing for growers, processors, dispensaries, transporters, labs, on-site consumption
- Enforces product testing, packaging, and labeling standards
- Operates Maryland's first state-run reference laboratory (launched March 2024)
- Conducts comprehensive public health tracking and reporting
- Publishes transparent sales data, license information, policy guidance
The 2025 Maryland Cannabis Use Biannual Study represents best-in-class market monitoring, examining consumption patterns, adverse outcomes, and policy impacts with academic rigor.
Alcohol, Tobacco, and Cannabis Commission (ATCC):
The ATCC's Field Enforcement Division enforces cannabis laws as they apply to unlicensed THC products, working in coordination with the MCA to ensure statewide compliance. The ATCC has authority to issue citations, seize non-compliant products, and prosecute violations for products sold outside the licensed cannabis system.
Seed-to-sale tracking:
Maryland uses Metrc for comprehensive inventory tracking—the gold standard system also employed by Colorado, Michigan, and Oregon. Every plant, batch, and sale is tracked from cultivation through retail, preventing diversion to illicit markets and enabling rapid recall if contamination detected.
Business and patient registration:
Maryland's OneStop business portal provides streamlined registration for all cannabis industry participants, including:
- Adult patient registration (18+ with qualifying conditions)
- Caregiver registration ($25, maximum 5 patients)
- Ancillary business registration ($500-7,500 for transporters, disposers)
- Clinical director registration
- Hospice patient registration
Testing requirements:
Mandatory comprehensive testing for all cannabis products:
- Potency analysis (THC, CBD, other cannabinoids)
- Pesticide screening (comprehensive panel)
- Heavy metals testing (lead, arsenic, cadmium, mercury)
- Microbial contaminants (E. coli, Salmonella, Aspergillus)
- Solvent residue testing for concentrates
- Mycotoxin screening
Maryland's testing is rigorous and enforced—creating genuine quality advantage over illicit products. The state's reference laboratory validates independent testing lab accuracy, addressing the testing fraud problem plaguing California.
Packaging and labeling standards:
Maryland requires comprehensive labeling under ABCA §36–203.1 and COMAR 14.17.18 including:
- Product identity and cannabinoid content
- Batch/lot numbers for traceability
- Health warnings and dosing information
- QR codes linking to lab test results (Certificate of Analysis)
- Child-resistant, tamper-evident packaging
- MCA-approved cannabis symbol on all products
- Cannot contain images appealing to children (candy, cartoons, animals, toys)
- Must avoid mimicking trademarked commercial products
Maryland extended these standards to hemp-derived THC products (Delta-8, Delta-9, Delta-10) via SB 214 effective July 2025, closing the gray market loophole that undermines legal cannabis in other states.
Home Cultivation: Maryland's Balanced Approach
Maryland allows limited home cultivation for both medical patients and adult-use consumers—striking reasonable balance between personal freedom and market protection.
Adult-use cultivation:
- Adults 21+ may cultivate up to 2 cannabis plants per household (regardless of number of adults)
- Out of public view (indoor or secured outdoor)
- Not accessible to minors
- On property lawfully possessed (owner consent required if renting)
- Secure from unauthorized access
Medical patient cultivation:
- Registered medical patients may cultivate up to 4 plants total (combining their adult-use and medical allowances)
Framework assessment:
Home cultivation minimally impacts retail sales—contrary to industry fears. Analysis across 18 states shows:
- Growing costs (equipment, utilities, time): $300-600 per harvest
- Retail equivalent: $150-250 for same quality/quantity
- Most consumers choose convenience over cultivation
Two-plant limit ensures home cultivation serves personal use (not commercial diversion) while providing affordable option for:
- Budget-conscious consumers (fixed-income, students)
- Rural residents (limited dispensary access)
- Hobbyists (gardening enthusiasts)
- Medical patients (specific strains unavailable retail)
Maryland's approach mirrors Colorado (6 plants), Michigan (12 plants), and Oregon (4 plants)—none of which experienced retail collapse due to home cultivation.
CBDT Framework Assessment: Maryland's Underperformance
The CBDT Framework reveals Maryland's market position and optimization potential.
Current performance: 60-68% legal market share
- Transaction share: Estimated 65-72% (percentage of users choosing legal over illicit for at least some purchases)
- Volume share: Estimated 60-68% (accounting for heavy user behavior patterns)
This represents solid mid-tier performance—significantly better than struggling markets (California 50%, New York 30%) but disappointing relative to Maryland's policy quality.
Comparison:
- Michigan: 85% (superior access, delivery, lower effective costs)
- Oregon: 82% (extreme price competitiveness)
- Colorado: 73-78% (mature optimization)
- Maryland: 60-68% (strong foundation, incomplete build)
- Illinois: 55-60% (high-tax disaster)
Maryland substantially outperforms Illinois despite similar demographics—proving low taxes enable better outcomes. But Maryland underperforms Michigan by 17-25 percentage points despite comparable policy approach—revealing access density and delivery authorization matter immensely.
CBDT Lever Analysis
Price Competitiveness (4× weight): MODERATE
Maryland legal prices 5-40% above illicit:
- Legal: $8.40/gram flower, $30-45/gram concentrate
- Illicit: $6-8/gram flower, $20-35/gram concentrate
The framework shows legal markets succeed when price premium stays below 20-25%. Maryland's range suggests:
- Casual consumers: Legal pricing acceptable (convenience + quality justify premium)
- Moderate consumers: Mixed behavior (legal for convenience, illicit for bulk)
- Heavy users: Predominantly illicit (40% premium unsustainable for high-volume)
Maryland's tax increase to 12% (July 2025) worsens price competitiveness by ~10%, pushing more heavy users toward illicit sources.
Without 280E federal penalty, Maryland prices would fall 12-18%, improving price competitiveness dramatically. Current moderate performance represents success despite federal handicap.
Access Density (2.8× combined weight): WEAK
- 102 dispensaries for 6.2M residents = 1.6 per 100K
- Optimal density: 2.5-3.5 per 100K
- No adult-use delivery permitted
- Rural/suburban areas significantly underserved
Michigan achieves 85% legal share with 6+ dispensaries per 100k plus statewide delivery. Maryland's 1.6 per 100k without delivery creates structural disadvantage—forcing consumers in underserved areas to choose illicit convenience over legal inconvenience.
Geographic analysis shows direct correlation: Baltimore-Washington corridor (high dispensary density) achieves 70-75% legal share. Eastern Shore/Western Maryland (low density) achieves only 45-55% legal share.
Convenience (includes payment friction): MODERATE
- Cash-dominant operations (Mastercard prohibited since Aug 2023)
- Some debit card access (Visa/Discover where available)
- No adult-use delivery (reduces convenience dramatically)
- Operating hours: 6 AM - midnight (reasonable but not 24-hour)
- Online ordering for pickup (but cash payment required)
Cash requirement reduces transaction frequency 12-18%. Delivery prohibition particularly harms rural consumers and mobility-impaired. Combined effect: 8-12 percentage point reduction in legal market share versus cashless + delivery scenario.
Safety/Quality (1.2× weight): EXCELLENT
Maryland excels in testing and quality assurance:
- Rigorous comprehensive testing (cannabinoid, pesticide, heavy metal, microbial)
- State reference laboratory validates testing accuracy (prevents fraud)
- Metrc seed-to-sale tracking ensures authenticity
- Professional dispensary operations create trustworthy environment
- Quality advantage over illicit market clear and substantial
Maryland's testing rigor matches Colorado and Oregon—far superior to California's testing fraud problem. This represents Maryland's greatest policy strength.
But quality advantage has limits: when legal costs 40%+ more than illicit, price-sensitive consumers accept moderate quality reduction for substantial savings. Quality matters most when price differential is narrow (10-20%).
Enforcement (0.6× weight): MODERATE
Maryland law enforcement focuses on:
- Large-scale illegal cultivation operations
- Interstate trafficking from source states
- Unlicensed dispensary operations (rare)
- Diversion from legal to illegal markets
Enforcement adequate but not aggressive. Not Nevada-level interdiction but not California-level abdication.
Market Fragmentation Penalty: MINIMAL
Maryland avoided California's fragmentation disaster through state preemption of most local bans. Maryland law limits municipal authority—jurisdictions can regulate zoning (1,000-foot buffers from schools, 1,000-foot spacing between dispensaries) but cannot prohibit licensed dispensaries outright.
Exception: Ocean City banned on-premises consumption licenses pre-emptively (June 2023), and other jurisdictions maintain zoning restrictions. But these represent minor constraints, not systemic fragmentation.
Result: Most of Maryland's 6.2 million residents have legal retail access within reasonable distance (though not optimal due to low dispensary count). Geographic gaps exist but limited compared to California (61% local bans) or New York (regulatory chaos).
The Framework Verdict
Maryland should achieve 72-78% legal market share with current state policy if federal barriers (280E, SAFE Banking) were removed.
Maryland achieves only 60-68% because:
- Federal 280E adds 12-18% to retail prices (price competitiveness reduced)
- SAFE Banking absence creates payment friction (12-18% transaction frequency reduction)
- Insufficient dispensary density (1.6 vs. optimal 2.5-3.5 per 100k)
- No adult-use delivery authorization (access gaps in underserved areas)
- Tax increase to 12% worsens competitiveness (effective July 2025)
The Maryland underperformance: 8-15 percentage points below potential given policy quality.
This translates to:
- $280-420M annual sales that should be legal (currently illicit)
- $55-85M lost tax revenue annually
- 3,000-4,500 jobs that don't exist
- Persistent illicit market undermining public safety and legitimate businesses
Maryland built excellent foundation. Now Maryland needs federal reform + state policy completion to capture the market its policies deserve.
Policy Recommendations: Completing Maryland's Success Story
Maryland policymakers must act at both state and federal levels to optimize the cannabis market they wisely initiated.
Priority #1: Federal Reform Advocacy
Schedule III Rescheduling (280E Elimination):
Maryland's congressional delegation should champion Schedule III as economic necessity for Maryland businesses and consumers.
Current Maryland impact:
- 280E costs Maryland cannabis businesses $38-55M annually in excess federal taxes
- Forces retail prices 12-18% higher than economically necessary
- Reduces legal market share by 5-8 percentage points
- Costs Maryland $55-85M in lost state tax revenue
Post-Schedule III projection:
- Maryland businesses save $38-55M annually
- Savings partially passed to consumers (10-15% price reductions)
- Legal market share improves to 68-76% within 18-24 months
- Maryland gains $60-95M in additional state tax revenue
SAFE Banking Act Passage:
Current Maryland impact:
- Cash operations create public safety risks (robbery targets)
- Payment friction reduces transaction frequency 12-18%
- Costs Maryland businesses $25-40M annually (security, elevated costs)
- Social equity licensees cannot access capital
Post-SAFE Banking projection:
- Card payment access increases transaction frequency 18-25%
- Maryland market grows $180-280M annually
- State tax revenue increases $16-25M annually
- Social equity access to commercial lending improves dramatically
Priority #2: Maintain 9% Tax Rate
Maryland must resist the July 2025 tax increase from 9% to 12%.
Why the increase is counterproductive:
Revenue optimization comes through volume (market share), not rates. Research demonstrates 10% price increases reduce cannabis purchases 8-12%.
The framework predicts:
- 3-point tax increase = ~10% retail price increase
- 10% price increase = 8-10% reduction in legal purchases
- Legal market share declines 2-3 percentage points
- Heavy users shift to illicit sources
- Net revenue impact: $27-32M annually (not projected $39M)
Better approach:
Maintain 9% tax but expand access (more dispensaries, delivery):
- More dispensaries = more transactions
- More transactions = more revenue despite same rate
- Market share grows instead of shrinks
Example:
- Current: 60-68% legal share × 9% tax = 5.4-6.1% effective revenue capture
- With 12% tax: 58-65% legal share × 12% tax = 7.0-7.8% effective revenue capture
- With 9% + expanded access: 70-76% legal share × 9% tax = 6.3-6.8% effective revenue capture
Expanding access generates comparable revenue without driving consumers to illicit markets.
Priority #3: Expand Dispensary Licensing
Maryland must authorize additional licensing rounds targeting underserved regions.
Geographic allocation approach:
Rather than statewide lottery, implement county-based allocation ensuring balanced distribution:
Target allocations (additional dispensaries needed):
- Eastern Shore: +15-20 dispensaries (Worcester, Wicomico, Dorchester, Talbot, Caroline, Kent)
- Western Maryland: +12-18 dispensaries (Washington, Allegany, Garrett)
- Southern Maryland: +15-20 dispensaries (Charles, Calvert, St. Mary's)
- Northern/Central rural: +18-22 dispensaries (Frederick, Carroll, Harford, Cecil)
Total expansion: 60-80 additional dispensaries reaching optimal 2.6-3.2 per 100k density.
Implementation timeline:
- Phase 1 (2026): Authorize 30-40 new licenses prioritizing most underserved counties
- Phase 2 (2027): Authorize 30-40 additional licenses filling remaining gaps
- Phase 3 (2028+): Market-driven expansion based on demand patterns
Social equity priority:
Continue prioritizing social equity applicants but provide meaningful support:
- Cannabis Business Assistance Fund expansion ($5-10M additional annually)
- Technical assistance program (MCA-funded consulting for licensees)
- Mentorship partnerships with existing operators
- Streamlined capital access (coordinate with financial institutions post-SAFE Banking)
Priority #4: Authorize Adult-Use Delivery
Maryland should pass legislation authorizing statewide adult-use cannabis delivery.
Recommended framework:
- License requirement: Only licensed transporters or dispensaries can deliver
- Vehicle tracking: GPS tracking integrated with Metrc system
- Age verification: Government ID scan at delivery (same as retail)
- Purchase limits: Same as retail (1.5 oz flower, 12g concentrate, 750mg edibles)
- Driver requirements: Background checks, training, no consumption on duty
- Geographic restrictions: None (statewide authorization)
- Cashless priority: Once SAFE Banking passes, enable card payments for delivery
Legislative path:
House Bill 5394 (2024) represented solid framework but failed committee. Revised legislation should:
- Address specific concerns raised (age verification, driver safety, diversion)
- Include sunset provision (5-year review to evaluate safety impacts)
- Phase implementation (initial limited rollout, expand after evaluation)
Maryland should reference Michigan, Massachusetts, Oregon, and 15+ other states' successful delivery programs.
Projected impact:
Delivery authorization would:
- Add $85-130M annually to legal market
- Increase legal market share 4-6 percentage points
- Reduce illicit market pressure in underserved areas
- Create 800-1,200 delivery jobs
- Generate $8-12M additional tax revenue annually
Priority #5: Maintain Hemp Regulation Enforcement
Maryland's July 2025 hemp-derived THC regulation (SB 214/HB 12) represents best practice—but enforcement critical.
Continue implementation:
- Alcohol, Tobacco, and Cannabis Commission conducts regular compliance inspections
- Coordinate with MCA on product testing standards
- Prosecute violations (unlicensed sales, age verification failures)
- Monitor online sales (out-of-state retailers shipping to Maryland)
- Utilize prima facie evidence powers (packaging/labeling as proof of violation)
Federal advocacy:
Maryland should join other states advocating for federal Farm Bill clarification:
- Define intoxicating hemp products as cannabis (not agricultural hemp)
- Require testing, labeling, age verification for all THC products
- Enable state regulation without federal preemption challenges
Unregulated hemp competition undermines Maryland's legal cannabis program, creating public safety risk and tax revenue erosion.
Optimized Scenario: What Maryland Could Achieve
With federal reform and state-level policy optimization, Maryland could transform from mid-tier performer to top-tier market.
Requirements for Optimization
Federal level:
- Schedule III rescheduling: Eliminates 280E, reduces retail prices 12-18%, improves legal share 5-8 points
- SAFE Banking Act: Enables card payments, increases transaction frequency 18-25%, improves legal share 4-6 points
State level:
- Maintain 9% tax rate: Resist July 2025 increase to 12%
- Expand dispensary licensing: Target 160-200 dispensaries (2.6-3.2 per 100k)
- Authorize adult-use delivery: Statewide with licensed transporter requirement
- Maintain hemp regulation: Continue SB 214/HB 12 enforcement
Predicted Outcomes (Optimized Policy + Federal Reform)
Timeline: 24-36 months after implementation
Legal market share:
- Transaction share: 78-84%
- Volume share: 75-82%
Economic impact:
Current state (2025):
- Legal market: $1.15-1.20B annually
- Illicit market: $680-820M
- Tax revenue: $103-108M (9% tax)
- Legal market share: 60-68%
Optimized state (post-reform):
- Legal market: $1.65-1.90B annually (+43-58% growth)
- Illicit market: $280-420M (60-65% reduction)
- Tax revenue: $148-171M annually (+43-58% despite maintaining 9% rate)
- Legal market share: 75-82%
- Jobs: 15,000-18,000 total (vs. current 10,000-12,000)
Price impact:
- Federal 280E elimination: Retail prices drop 12-18%
- SAFE Banking: Operating costs decline 8-12% (reduced security, banking fees)
- Combined effect: Average item price falls from $27-28 to $21-24
- Legal cannabis becomes genuinely price-competitive with illicit ($6-8/gram)
Access impact:
- Expanded licensing: 160-200 dispensaries reduce average travel time 30-40%
- Delivery authorization: Rural/suburban consumers gain convenient access
- Combined effect: Legal option matches illicit convenience in most markets
Social equity impact:
- SAFE Banking enables capital access for social equity licensees
- 280E elimination allows small businesses to achieve profitability
- Market expansion creates opportunity for new entrants
- Reduced prices make legal cannabis accessible to disadvantaged communities
Maryland would achieve outcomes comparable to:
- Michigan: 85% legal share (superior access)
- Colorado: 84-88% with federal reform (mature optimization)
- Oregon: 82% (extreme price competitiveness)
This represents the market Maryland's policies deserve—capturing vast majority of demand through competitiveness, convenience, and quality.
Comparison to Other Markets
Maryland's 60-68% legal market share represents solid mid-tier performance—neither exceptional nor failing.
High-performing markets (75%+):
Michigan (85% volume):
- Moderate taxes (16% total)
- Extensive access (600+ dispensaries = 6 per 100k)
- Statewide delivery authorized
- Competitive pricing ($6-8/gram)
- Why Michigan excels: Aggressive access expansion + moderate taxes
Oregon (82% volume):
- Lowest taxes (17% total)
- Extreme access (16.8 dispensaries per 100k)
- Legal prices below illicit in many markets
- Strong enforcement
- Why Oregon leads: Oversupply creates price competition
Colorado (73-78% volume, projected 84-88% with federal reform):
- Moderate taxes (15% retail excise)
- Mature infrastructure (11+ years operational)
- Minimal fragmentation
- Home cultivation permitted
- Why Colorado succeeds: Balanced policy, pioneer experience
Mid-tier markets (60-75%):
Maryland (60-68% volume) — current:
- Very low taxes (9%, increasing to 12%)
- Insufficient access (1.6 dispensaries per 100k)
- No adult-use delivery
- Strong quality standards
- With federal reform: Could reach 75-82%
Minnesota (projected 68-75%):
- New market (opened July 2023)
- Moderate taxes
- Learning from other states' mistakes
- Cautious but thoughtful expansion
Washington (65% volume, declining):
- Very high taxes (37% flat excise)
- Mature market fatigue
- No home cultivation
- Similar tax policy error to Maryland's pending increase
Struggling markets (30-60%):
Illinois (55-60% volume):
- Extremely high taxes (25-40%)
- Social equity rhetoric without economic competitiveness
- Price uncompetitive
- Declining toward California performance
California (50% volume):
- Very high taxes (28-35%)
- Massive fragmentation (61% local bans)
- Testing fraud
- Minimal enforcement
- Policy disaster despite ideal conditions
New York (30% volume):
- Regulatory chaos
- Insufficient retail (250 stores for 20M people)
- Enforcement abdication
- Unlicensed shops tolerated
- Worst major market performance
Maryland's Position
Maryland substantially outperforms dysfunction cases (California, New York, Illinois) through:
- Low taxes (9% vs. 25-40%)
- Professional regulation (MCA vs. chaos)
- Minimal fragmentation (state preemption vs. local bans)
- Quality standards (testing enforcement vs. fraud)
But Maryland underperforms Michigan by 17-25 percentage points despite comparable demographics and policy approach. The difference:
- Michigan: 6 dispensaries per 100k + delivery = 85% legal share
- Maryland: 1.6 dispensaries per 100k + no delivery = 60-68% legal share
Access density and delivery matter enormously. Maryland proved this through excellent policy design—now must complete implementation.
Timeline and Economic Projections
Phase 1 (Current — 2026): Stable Growth, Policy Pressure
Focus:
- Continue operating under current framework
- Resist 12% tax increase (maintain 9%)
- Social equity licensees gradually operationalize
- Federal advocacy for Schedule III and SAFE Banking
Expected market performance:
- Legal market: $1.15-1.25B annually (3-5% growth)
- Legal market share: 60-68% (flat to slight decline if tax increases)
- Tax revenue: $103-113M annually (at 9% tax)
- Jobs: 10,000-13,000
Key challenge: Tax increase to 12% (July 2025) would reduce market share 2-3 points and drive heavy users to illicit sources.
Phase 2 (2026-2027): Schedule III Implementation
Assumes: DEA completes Schedule III rescheduling (likely 2025-2027)
Impact:
- Maryland businesses save $38-55M annually in federal taxes
- Savings partially passed to consumers (10-15% retail price reductions)
- Price competitiveness improves significantly
Market response:
- Price-sensitive consumers shift from illicit to legal
- Transaction frequency increases
- Heavy users begin returning to legal market
Predicted outcomes (12-18 months post-implementation):
- Legal market: $1.40-1.60B annually (+22-37%)
- Legal market share: 68-74% (+8-12 points)
- Tax revenue: $126-144M annually (+22-37%)
- Jobs: 13,000-16,000 (+3,000-6,000)
Schedule III alone provides substantial improvement but insufficient for optimization—state-level action still required.
Phase 3 (2027-2029): SAFE Banking + State Expansion
Assumes:
- SAFE Banking Act passes
- Maryland expands licensing to 160-200 dispensaries
- Maryland authorizes adult-use delivery
Impact:
- Card payment access increases transaction frequency 18-25%
- Expanded dispensary network reduces travel time/increases convenience
- Delivery enables access for underserved areas
- Social equity access to capital improves
Combined effect:
Maryland legal cannabis achieves genuine price competitiveness and convenience parity with illicit alternatives:
- Current legal: $27-28 per item
- Post-reform legal: $21-24 per item
- Illicit: $18-22 per item equivalent
- Legal premium: 10-15% (acceptable for quality/convenience)
Market response:
- Heavy users transition to legal market
- Rural/suburban consumers gain convenient access
- Legal market captures both transaction share and volume share
Predicted outcomes (12-24 months post-implementation):
- Legal market: $1.65-1.90B annually (+18-30% from Phase 2)
- Legal market share: 75-82% (+7-15 points from Phase 2)
- Tax revenue: $148-171M annually (at 9% tax)
- Jobs: 15,000-18,000 (+2,000-5,000 from Phase 2)
- Illicit market: Reduced from $680-820M to $280-420M
Phase 4 (2029-2032): Optimized Steady State
Characteristics:
- Mature market with federal support
- Price-competitive legal cannabis
- Comprehensive access (retail + delivery)
- Thriving social equity sector
Sustained outcomes:
- Legal market: $1.75-2.05B annually (inflation-adjusted growth)
- Legal market share: 75-82% (sustained)
- Tax revenue: $157-185M annually
- Jobs: 16,000-19,000
Remaining illicit market (18-25%):
- Extreme price-sensitive heavy users (~8-10%)
- Personal cultivation networks (~3-4%)
- Geographic gaps (very rural) (~2-3%)
- Social/cultural illicit preference (~5-8%)
This represents Maryland's optimization ceiling—further improvement requires price reductions below economically sustainable levels or enforcement increases politically infeasible.
Economic Reality: Current Trajectory vs. Optimized Scenario
Current trajectory (No federal reform, 12% tax implemented):
2025-2030 projection:
- Legal market growth slows: $1.15-1.30B annually
- Market share erodes: 58-65% by 2030 (12% tax drives consumers away)
- Tax revenue disappoints: $138-156M annually (higher rate, lower volume)
- Illicit market expands: $720-880M persistent
- Social equity struggles: Capital barriers prevent most licensees from thriving
Cumulative lost opportunity (2025-2030):
- Lost tax revenue vs. optimized: $220-340M over 5 years
- Lost jobs: 5,000-8,000 vs. optimized scenario
- Persistent illicit market: $3.6-4.4B in black market activity over 5 years
- Social equity failure: Intended beneficiaries excluded from market success
Optimized scenario (Schedule III + SAFE Banking + state expansion):
2025-2030 projection:
- Legal market grows: $1.75-2.05B by 2030
- Market share improves: 75-82%
- Tax revenue increases: $157-185M annually by 2030 (despite maintaining 9%)
- Illicit market shrinks: $280-420M
- Jobs created: +6,000-9,000 from current
- Social equity success: Legal market accessible and profitable for disadvantaged communities
Cumulative benefit (2025-2030):
- Additional tax revenue: $220-340M over 5 years
- Additional jobs: 6,000-9,000 created/sustained
- Reduced illicit market: $2-3B in black market eliminated over 5 years
- Economic multiplier: $350-550M in broader economic activity
The Difference
Federal reform + state policy completion is worth $45-70M annually to Maryland in tax revenue alone, plus 6,000-9,000 jobs, plus massive public safety improvement through illicit market reduction.
Maryland built the foundation. Federal reform + state expansion completes the structure, capturing the market Maryland's policies deserve.
Conclusion: Maryland Must Complete What It Started
Maryland achieved what seemed impossible in 2023: launching adult-use cannabis sales smoothly, professionally, and successfully—avoiding the chaos that plagued California, New York, and Illinois.
The state implemented low taxes (9%), quality standards (rigorous testing), minimal fragmentation (state preemption of local bans), and professional regulation (Maryland Cannabis Administration). Eighteen months later, $1.14 billion in annual sales and stable market growth vindicate the approach.
But Maryland made a critical error: it stopped building before finishing.
With only 102 dispensaries serving 6.2 million residents (1.6 per 100,000 versus optimal 2.5-3.5), no adult-use delivery authorization, and crippling federal barriers (280E tax penalty and banking restrictions), Maryland achieves 60-68% legal market share—solid compared to struggling markets but disappointing relative to policy quality.
The CBDT Framework reveals Maryland's underperformance: 8-15 percentage points below potential. That gap represents:
- $280-420M in annual sales remaining illicit (should be legal)
- $55-85M in lost tax revenue annually
- 3,000-4,500 jobs that don't exist
- Persistent black market undermining public safety
This outcome wasn't inevitable. Maryland chose cautious licensing and delayed delivery—prioritizing orderly rollout over aggressive optimization. The result: excellent foundation, incomplete structure.
Contrast with Michigan: similar population, similar demographics, but Michigan achieves 85% legal market share through 600+ dispensaries (6 per 100k), statewide delivery, and competitive pricing. Maryland could match or exceed Michigan's performance—the policies needed are straightforward:
Federal level:
- Schedule III rescheduling: Eliminates 280E, reduces prices 12-18%, adds 5-8 points to legal share
- SAFE Banking Act: Enables card payments, increases transactions 18-25%, adds 4-6 points to legal share
- Maryland's congressional delegation should champion both as economic necessities
State level:
- Maintain 9% tax (resist July 2025 increase to 12%)
- Expand licensing to 160-200 dispensaries (prioritize underserved regions)
- Authorize adult-use delivery statewide
- Support social equity licensees (capital access, technical assistance)
- Continue SB 214 enforcement (hemp-derived THC regulation)
- Implement SB 215 (on-site consumption venues)
With these reforms, Maryland would improve from 60-68% to 75-82% legal market share within 24-36 months, generating:
- $1.65-1.90B annually in legal cannabis sales
- $148-171M in tax revenue (despite maintaining 9% rate—volume drives revenue)
- 15,000-18,000 jobs
- $280-420M illicit market (down from $680-820M)
The political challenge: Maryland faces budget pressure, creating temptation to raise taxes seeking immediate revenue. But the framework proves this thinking is economically backward. Revenue optimization comes through volume (market share), not rates.
Colorado generates more per-capita cannabis tax revenue than Maryland with 15% retail excise (versus Maryland's pending 12%) because Colorado captures 73-78% market share (versus Maryland's 60-68%). Lower taxes + higher market share = more total revenue.
Maryland should learn from Washington's error: high taxes during budget crisis generate short-term revenue but create long-term market erosion. Better approach: maintain 9% tax, expand access, capture market share—revenue follows naturally.
Maryland pioneered best practices in East Coast cannabis legalization. The state demonstrated that:
- Low taxes enable price competitiveness
- Professional regulation prevents chaos
- Minimal fragmentation ensures access
- Quality standards create genuine advantage
- Smooth launches reduce illicit market entrenchment
Now Maryland must pioneer the next step: federal reform advocacy combined with state-level policy completion.
The framework shows the path. Maryland built the foundation exceptionally well—evidence that competent policymaking produces results. The question is whether Maryland will complete construction or leave the building half-finished.
Maryland launched the best adult-use cannabis market in East Coast history. Now Maryland must perfect it.
CBDT Framework Citation
This analysis applies the Consumer-Driven Black Market Displacement Framework:
The Silent Majority 420, "Consumer-Driven Black Market Displacement (CBDT) Framework: A Behavioral-Utility Heuristic for Illicit-to-Legal Market Transition," Zenodo, 2025. DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.17593077
Validation data: Harvard Dataverse, DOI: 10.7910/DVN/MDVDTQ
Related Analyses: Idaho | Tennessee | N Carolina | Kansas
The Silent Majority 420 is an independent cannabis policy analyst. The CBDT Framework represents the first validated consumer-utility model for predicting market outcomes in vice legalization.
Analysis licensed CC BY 4.0
